Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Suppose we want to create an application whereby one can input their birthdate and the program will calculate their age.
We will be building an age calculator using Tkinter. Tkinter is the standard library in Python used to create Graphical User interfaces (GUIs). We will also import the datetime module, which supplies classes for manipulating dates and times.
Importing required modules
We will first install the modules needed from the command line interface.
pip install tkinter
datetime is a built-in Python module. We do not need to install it as it is already there.
Next, we import the modules in our code editor.
from tkinter import *
from datetime import date, datetime
We are importing all libraries in the tkinter module. We also import date and datetime libraries from datetime module.
Designing the interface
We will then design what our age calculator interface will look like. We will be using some of the tkinter widgets:
- Label - a widget used to specify the display boxes where we can place the text or images.
- Button - is used to add buttons that can display texts or images that convey the purpose of the buttons.
- Entry - a widget used to accept single-line text strings from a user.
root = Tk() #initializes tkinter to create display window
root.geometry('500x300') # width and height of the window
root.resizable(0, 0) # sets fix size of window
root.title(' Age calculator') # gives the window a title
#the rest of the code
root.mainloop()
We first create a tkinter instance called root, which aids in the display of the root window and manages all of the other tkinter application components. We then set the width and height of the window, and give it a title. The mainloop() method runs the script and displays the output window.
yourAge = Label(root,fg="red",text = "Date Month Year",font='arial 12 bold').place(x = 210)
setYourAlarm = Label(root,text = "Enter birthday: ",bg="grey",font="arial 11 bold").place(x=80, y=40)
date = StringVar()
month = StringVar()
year = StringVar()
dateTime= Entry(root,textvariable = date, relief = RAISED, width = 4,font=(20)).place(x=210,y=40)
monthTime= Entry(root,textvariable = month,width = 4,font=(20)).place(x=270,y=40)
yearTime = Entry(root,textvariable = year,width = 4,font=(20)).place(x=330,y=40)
We create label widgets, which will display where the date, month, and year data will be input.
StringVar() is used to edit a widget's text, and determine whether they have been read, overwritten, or do not exist at all. We create entry widgets for the date, month, and year where one will input their birthday. StringVar() then holds the string data.
place() method allows us to position our widgets by setting corresponding x and y values.
The interface so far looks like this:
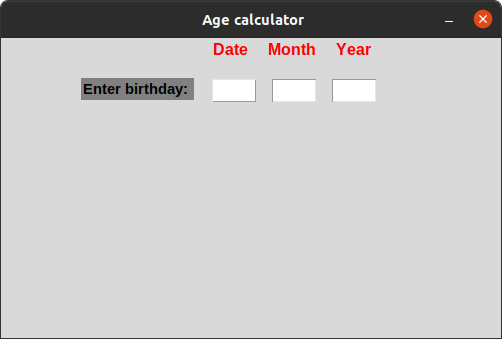
Adding age function
def age():
# Get current date
today = datetime.today().date()
setAge_year = int(year.get())
setAge_month = int(month.get())
setAge_date = int(date.get())
current_age = today.year-int(setAge_year)
if today.month < setAge_month or today.month == setAge_month and today.day < setAge_date:
current_age -= 1
CurrentLabel = Label(root, text=f'You are: {current_age} years old',fg='black')
CurrentLabel.place(relx=0.2, rely=0.8, anchor=CENTER)
We first define a function age. We then get the current date by using the datetime method. The function then gets the three entries and finds the difference between the current year and the input year. It then checks to make sure that the input month and date are greater than the current month and date. If not, it means the current age is less by one year.
We then create a label widget that will display the user's age.
Creating buttons
We then create two buttons, one which the user clicks to get their age, and another which when clicked destroys the window.
submit = Button(root,text = "Calculate your age",fg="red",width = 20,command=age,font=("arial 15 bold" )).place(x=90,y=100)
exit = Button(root,text = "Exit",fg="red",width = 10,command=root.destroy,font=("arial 20 bold" )).place(x=150,y=140)
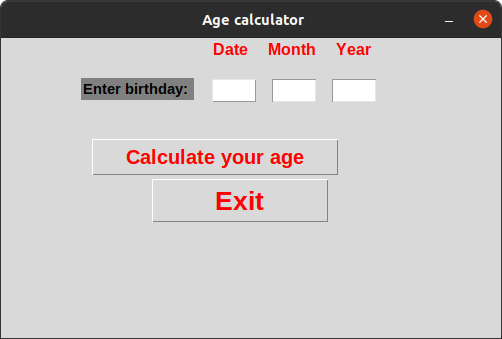
The final interface will be:
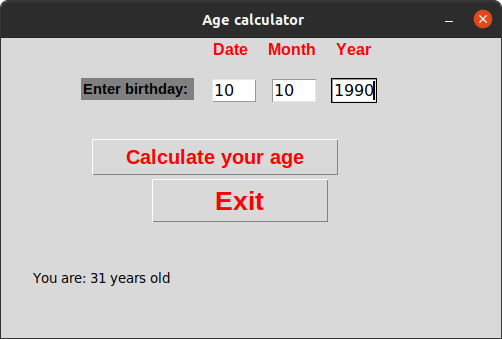
When we input date, month, and year, it calculates the age.
The complete code is:
from tkinter import *
from datetime import date, datetime
root = Tk() #initializes tkinter to create display window
root.geometry('500x300') # width and height of the window
root.resizable(0, 0) # sets fix size of window
root.title(' Age calculator') # gives the window a title
yourAge = Label(root,fg="red",text = "Date Month Year",font='arial 12 bold').place(x = 210)
setYourAlarm = Label(root,text = "Enter birthday: ",bg="grey",font="arial 11 bold").place(x=80, y=40)
date = StringVar()
month = StringVar()
year = StringVar()
dateTime= Entry(root,textvariable = date, relief = RAISED, width = 4,font=(20)).place(x=210,y=40)
monthTime= Entry(root,textvariable = month,width = 4,font=(20)).place(x=270,y=40)
yearTime = Entry(root,textvariable = year,width = 4,font=(20)).place(x=330,y=40)
def age():
# Get current date
today = datetime.today().date()
setAge_year = int(year.get())
setAge_month = int(month.get())
setAge_date = int(date.get())
current_age = today.year-int(setAge_year)
if today.month < setAge_month or today.month == setAge_month and today.day < setAge_date:
current_age -= 1
CurrentLabel = Label(root, text=f'You are: {current_age} years old',fg='black')
CurrentLabel.place(relx=0.2, rely=0.8, anchor=CENTER)
submit = Button(root,text = "Calculate your age",fg="red",width = 20,command=age,font=("arial 15 bold" )).place(x=90,y=100)
exit = Button(root,text = "Exit",fg="red",width = 10,command=root.destroy,font=("arial 20 bold" )).place(x=150,y=140)
root.mainloop()
Conclusion
We have successfully created an age calculator in python using tkinter. Happy coding.

